“`html
H. Pylori Diet: A Comprehensive Guide for Modern Health in 2025


Understanding H. Pylori and Its Effects on Digestive Health
The bacterium Helicobacter pylori, commonly referred to as H. pylori, can significantly impact digestive health. It is essential to understand the relationship between H. pylori and the symptoms it induces, such as chronic abdominal pain, bloating, and nausea. Managing H. pylori symptoms requires a multifaceted approach, including the H. pylori diet. This diet focuses on foods that promote gut health and minimize symptoms associated with H. pylori infection.
What Are the Symptoms of H. Pylori Infection?
H. pylori infection can lead to a variety of distressing symptoms. Common signs include persistent stomach pain, heartburn, and unexplained weight loss. Moreover, individuals with H. pylori may experience indigestion and bloating after meals. Recognizing these symptoms is crucial for timely diagnosis and management. A long-term presence of H. pylori can lead to more severe conditions, including gastritis and ulcers, necessitating immediate dietary modifications to alleviate these effects and support recovery.
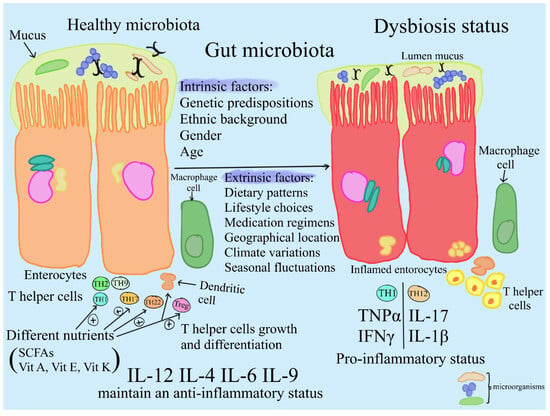
The Link Between H. Pylori and Gut Health
Gut health is paramount in managing H. pylori infection. Maintaining a balanced gut microbiome is essential for fighting off this bacterium. Specific foods to eat with H. pylori can enhance gut flora, support digestion, and reduce inflammation. Incorporating fermented foods for H. pylori like yogurt, kefir, and sauerkraut can naturally introduce beneficial bacteria into the digestive system, fostering biological resistance against H. pylori.
Food Choices: What to Include in the H. Pylori Diet
Choosing the right foods is vital to managing H. pylori. The best foods for H. pylori offer anti-inflammatory and immune-boosting properties. By focusing on a well-curated nutrition plan for H. pylori, individuals can bolster their bodies’ ability to combat this infection. This section will discuss key nutrients, optimal food sources, and diet recipes for H. pylori that contribute to a healthier digestive system.
Healing Foods for H. Pylori
Incorporating healing foods into your diet can facilitate a robust response against H. pylori. Foods rich in antioxidants, such as berries, broccoli, and leafy greens, play a crucial role in reducing oxidative stress within the body. Additionally, incorporating foods rich in omega-3s, such as fatty fish and flaxseeds, can decrease inflammation and promote healing in the gut lining, further challenging H. pylori’s persistence.
Anti-Inflammatory Foods to Consider
An anti-inflammatory diet for H. pylori not only helps alleviate symptoms but also curtails the inflammatory response triggered by H. pylori. Incorporating turmeric, ginger, and garlic into meals can enhance their health benefits. These spices contain potent compounds that support digestive health and enhance immune functioning, essential when dealing with this bacterium.
Probiotics and H. Pylori Management
Probiotics have garnered attention as a valuable component in the fight against H. pylori. Foods high in probiotics, such as kombucha, kimchi, and miso, enrich the gut microbiome, offering an advantageous environment that may inhibit H. pylori growth. Recent studies highlight the effectiveness of probiotics for H. pylori in enhancing eradication therapy and minimizing symptoms associated with the infection.
Foods to Avoid with H. Pylori
To improve digestive health, certain foods should be avoided in the dietetics for H. pylori sphere. These include processed foods high in sugar and acidity, as these can exacerbate symptoms and irritation. Identifying foods to avoid with H. pylori is crucial for maintaining a balanced gut environment and should be a focal point when crafting an effective dietary strategy against H. pylori.
High-Acidity Foods and Their Impact
High-acidity foods can significantly impact individuals with H. pylori. Consuming citrus fruits and tomato-based products can aggravate stomach acidity, leading to discomfort. This is why adhering to a low-acid diet for H. pylori can be beneficial in managing symptoms. Opting for alternatives such as bananas and coconuts may help in neutralizing stomach acidity while providing essential nutrients.
Refined Sugars and Processed Foods
Processed snacks, sugary beverages, and refined carbohydrates can disturb the balance of gut microbiota, making it easier for H. pylori to thrive. A low-sugar diet for H. pylori not only helps mitigate inflammation but also reduces symptom severity, promoting a healthier digestive ecosystem. Reinforcing whole foods into daily meals while minimizing sugar intake will aid in achieving long-term gut health.
Practical Recommendations for H. Pylori Management
Managing H. pylori involves holistic care, including lifestyle changes. It is critical to develop lifestyle changes for H. pylori that focus on nutrition, stress management, and supportive supplements. This section will explore practical steps that individuals can implement today to enhance their overall health and support H. pylori treatment.
Meal Planning Strategies for H. Pylori
A well-structured meal plan can alleviate symptoms and improve overall digestive health. When planning meals for H. pylori, focus on including fiber-rich foods for H. pylori and incorporating gentle cooking methods such as steaming or baking. Meal prep can help eliminate the temptation of poor food choices, ensuring healthy, nutritious options are readily available.
Hydration Tips and Their Role
Staying adequately hydrated is vital for digestive health and plays a role in H. pylori management. Hydration aids in supporting digestion and eliminating toxins. Including herbal teas, low-sugar health drinks, and clear fluids can promote overall wellness and assist in managing H. pylori by creating an unfavorable environment for the bacteria to thrive.
Key Takeaways for the H. Pylori Diet
- Focus on anti-inflammatory and gut-healing foods to manage H. pylori symptoms.
- Avoid high-acidity and sugar-laden foods to support gut health.
- Incorporate probiotics and fiber-rich foods to enhance the gut microbiome.
- Implement mindful eating and meal planning for symptom management.
- Stay hydrated and consider stress management techniques alongside dietary changes.
FAQ
1. What are the best foods for H. pylori?
Foods like garlic, ginger, and green leafy vegetables are among the best foods for H. pylori. These ingredients possess anti-inflammatory properties and can enhance gut health, making them excellent choices for individuals managing H. pylori symptoms.
2. How does diet influence H. pylori treatment?
A well-planned diet significantly supports H. pylori treatment by providing nutrients necessary for recovery, reducing inflammation, and maximizing the effectiveness of any eradication therapy prescribed by healthcare providers.
3. Can probiotics help with H. pylori management?
Yes, studies have shown that incorporating probiotics for H. pylori in your daily routine can improve gut flora balance, decrease H. pylori presence, and reduce associated symptoms.
4. What lifestyle changes can help with my H. pylori symptoms?
Making lifestyle changes such as managing stress through mindfulness, staying hydrated, and adhering to a nutritious meal plan can significantly improve H. pylori symptoms while promoting digestive health.
5. What common foods should I avoid if I have H. pylori?
Avoiding high-acid foods, refined sugars, and processed products can help manage symptoms. These foods can irritate the stomach lining and exacerbate H. pylori-related issues.
6. How can I incorporate cooking methods that retain nutritional value?
Utilizing gentle cooking methods, such as steaming or sautéing, helps preserve the nutritional content of your food, which is particularly beneficial on an H. pylori diet, ensuring you get essential vitamins and minerals.
7. Is it important to discuss dietary changes with my doctor?
Yes, consulting with a healthcare provider before making significant dietary changes is essential, especially when dealing with H. pylori. They can offer personalized advice and adjustments to maximize health benefits based on your needs.
“`